|
|
|
|
|
|
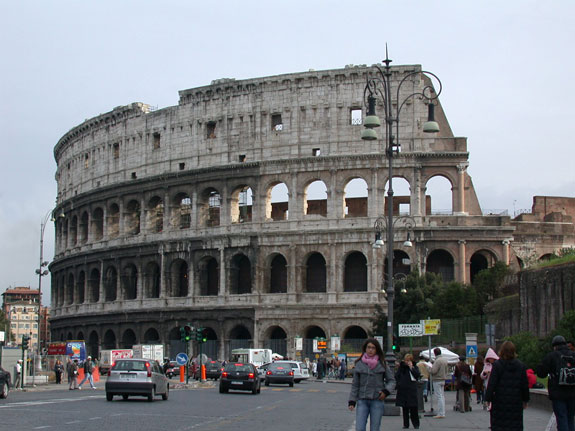


Coliseum
It was built during the reign of Emperor Vespasiano c. 72 AD and dedicated in 80 AD by his son Titus. The popular name of Coliseumcame about because the immense oval stadium was situated next to a colossal statue of Nero. The original name of this ancient Roman sports arena, the largest arena of its kind, is The Amphitheatrum Flavium.
Over 160 ft high with eighty entrances, the Coliseum could hold upwards of 50,000 spectators. Public events such as gladiator fights, mock naval battles and wild animal hunts were held at the Coliseum. During the staged fights as many as 10,000 people were killed. Fighters were slaves, prisoners or volunteers. Spectators saw persecuted Christians killed by lions. After 404 AD gladiatorial battles were no longer held, but animals such as lions, elephants, snakes and panthers continued to be massacred in the name of sport until the 6th century. Mock naval battles were arranged by removing the heavy wooden flooring and flooding the lower cells, which usually housed the animals and prisoners. As gladiator fights proved to be more popular, the naval battles were ultimately moved to another site, and the wooden floors made permanent. During the middle ages, stones from the Coliseum were removed for new buildings. From the fourth story of the Coliseum wooden masts supported a linen awning that protected spectators from the sun. The Coliseum boasted seats of marble for the upper class, and benches of wood for the lower. Ramps within the arena made movement easy by the large crowds, and on a catwalk suspended above, trained archers were watchful and would shoot to avert disaster when an enraged animal would get out of hand. A wall about 15 feet high separated the spectators from the bloody events in the arena. Today, in Rome, the Coliseum is one of its most famous landmarks and tourist attractions. Although it survives only as a ruin, it still rates as one of the finest examples of Roman architecture and engineering.
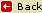
|
|
|
|